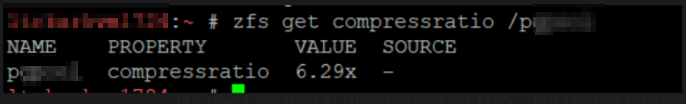
We’ve got several PostgreSQL servers using ZFS file system for the database, and I needed to know how compressed the data is. Fortunately, there appears to be a zfs command that does exactly that: report the compression ratio for a zfs file system. Use zfs get compressratio /path/to/mount
Tag: Linux
Linux – High Load with CIFS Mounts using Kernel 6.5.5
We recently updated our Fedora servers from 36 and 37 to 38. Since the upgrade, we have observed servers with very high load averages – 8+ on a 4-cpu server – but the server didn’t seem unreasonably slow. On the Unix servers I first used, Irix and Solaris, load average counts threads in a Runnable state. Linux, however, includes both Runnable and Uninterruptible states in the load average. This means processes waiting – on network calls using mkdir to a mounted remote server, local disk I/O – are included in the load average. As such, a high load average on Linux may indicate CPU resource contention but it may also indicate I/O contention elsewhere.
But there’s a third possibility – code that opts for the simplicity of the uninterrupted sleep without needing to be uninterruptible for a process. In our upgrade, CIFS mounts have a laundromat that I assume cleans up cache – I see four cifsd-cfid-laundromat threads in an uninterruptible sleep state – which means my load average, when the system is doing absolutely nothing, would be 4.
2023-10-03 11:11:12 [lisa@server01 ~/]# ps aux | grep " [RD]" USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1150 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? D Sep28 0:01 [cifsd-cfid-laundromat] root 1151 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? D Sep28 0:01 [cifsd-cfid-laundromat] root 1152 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? D Sep28 0:01 [cifsd-cfid-laundromat] root 1153 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? D Sep28 0:01 [cifsd-cfid-laundromat] root 556598 0.0 0.0 224668 3072 pts/11 R+ 11:11 0:00 ps aux
Looking around the Internet, I see quite a few bug reports regarding this situation … so it seems like a “ignore it and wait” problem – although the load average value is increased by these sleeping threads, it’s cosmetic. Which explains why the server didn’t seem to be running slowly even through the load average was so high.
https://lkml.org/lkml/2023/9/26/1144
Date: Tue, 26 Sep 2023 17:54:10 -0700 From: Paul Aurich Subject: Re: Possible bug report: kernel 6.5.0/6.5.1 high load when CIFS share is mounted (cifsd-cfid-laundromat in"D" state) On 2023-09-19 13:23:44 -0500, Steve French wrote: >On Tue, Sep 19, 2023 at 1:07 PM Tom Talpey <tom@talpey.com> wrote: >> These changes are good, but I'm skeptical they will reduce the load >> when the laundromat thread is actually running. All these do is avoid >> creating it when not necessary, right? > >It does create half as many laundromat threads (we don't need >laundromat on connection to IPC$) even for the Windows server target >example, but helps more for cases where server doesn't support >directory leases. Perhaps the laundromat thread should be using msleep_interruptible()? Using an interruptible sleep appears to prevent the thread from contributing to the load average, and has the happy side-effect of removing the up-to-1s delay when tearing down the tcon (since a7c01fa93ae, kthread_stop() will return early triggered by kthread_stop). ~Paul
Maintaining an /etc/hosts record
I encountered an oddity at work — there’s a server on an internally located public IP space. Because it’s public space, it is not allowed to communicate with the internal interface of some of our security group’s servers. It has to use their public interface (not technically, just a policy on which they will not budge). I cannot just use a DNS server that resolves the public copy of our zone because then we’d lose access to everything else, so we are stuck making an /etc/hosts entry. Except this thing changes IPs fairly regularly (hey, we’re moving from AWS to Azure; hey, let’s try CloudFlare; nope, that is expensive so change it back) and the service it provides is application authentication so not something you want randomly falling over every couple of months.
So I’ve come up with a quick script to maintain the /etc/hosts record for the endpoint.
# requires: dnspython, subprocess
import dns.resolver
import subprocess
strHostToCheck = 'hostname.example.com' # PingID endpoint for authentication
strDNSServer = "8.8.8.8" # Google's public DNS server
listStrIPs = []
# Get current assignement from hosts file
listCurrentAssignment = [ line for line in open('/etc/hosts') if strHostToCheck in line]
if len(listCurrentAssignment) >= 1:
strCurrentAssignment = listCurrentAssignment[0].split("\t")[0]
# Get actual assignment from DNS
objResolver = dns.resolver.Resolver()
objResolver.nameservers = [strDNSServer]
objHostResolution = objResolver.query(strHostToCheck)
for objARecord in objHostResolution:
listStrIPs.append(objARecord.to_text())
if len(listStrIPs) >= 1:
# Fix /etc/hosts if the assignment there doesn't match DNS
if strCurrentAssignment in listStrIPs:
print(f"Nothing to do -- hosts file record {strCurrentAssignment} is in {listStrIPs}")
else:
print(f"I do not find {strCurrentAssignment} here, so now fix it!")
subprocess.call([f"sed -i -e 's/{strCurrentAssignment}\t{strHostToCheck}/{listStrIPs[0]}\t{strHostToCheck}/g' /etc/hosts"], shell=True)
else:
print("No resolution from DNS ... that's not great")
else:
print("No assignment found in /etc/hosts ... that's not great either")
Mounting DD Raw Image File
And a final note from my disaster recovery adventure — I had to use ddrescue to copy as much data from a corrupted drive as possible (ddrescue /dev/sdb /mnt/vms/rescue/backup.raw –try-again –force –verbose) — once I had the image, what do you do with it? Fortunately, you can mount a dd file and copy data from it.
# Mounting DD image
2023-04-17 23:54:01 [root@fedora /]# kpartx -l backup.raw
loop0p1 : 0 716800 /dev/loop0 2048
loop0p2 : 0 438835200 /dev/loop0 718848
2023-04-17 23:55:08 [root@fedora /]# mount /dev/mapper/loop0p2 /mnt/recovery/ -o loop,ro
mount: /mnt/recovery: cannot mount /dev/loop1 read-only.
dmesg(1) may have more information after failed mount system call.
2023-04-17 23:55:10 [root@fedora /]# mount /dev/mapper/loop0p2 /mnt/recovery/ -o loop,ro,norecovery
2023-04-18 00:01:03 [root@fedora /]# ll /mnt/recovery/
total 205G
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 213 Jul 14 2021 .
drwxr-xr-x. 8 root root 123 Apr 17 22:38 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 127G Apr 17 20:35 ExchangeServer.qcow2
-rw-r--r--. 1 qemu qemu 10G Apr 17 21:42 Fedora.qcow2
-rw-r--r--. 1 qemu qemu 15G Apr 17 14:05 FedoraVarMountPoint.qcow2
Repairing Corrupt Partitions
After the power came back on, I had to recover ext and xfs partitions —
# FSCK to clean up bad superblock
lsblk
fsck /dev/sdb
e2fsck -b 32768 /dev/sdb1
mount /dev/sdb1 /var
# xfs_repair for XFS FS on LVM
lvscan # get dev for LVM
mount /dev/fedora/root /mnt/oh
xfs_repair -L /dev/fedora/root
mount /dev/fedora/root /mnt/oh
Mounting a QCOW File
We had a power outage on Monday that took out the drive that holds our VMs. There are backups, but the backup drive copies had superblock errors and all sorts of issues. To recover our data, I learned all sorts of new things — firstly that you can mount a QCOW file and copy data out. First, you have to connect a network block device to the file. Once it is connected, you can use fdisk to list the partitions on the drive and mount those partitions. In this example, I had a partition called nbd0p1 that I mounted to /mnt/data_recovery
modprobe nbd max_part=2
qemu-nbd --connect=/dev/nbd0 /path/to/server_file.qcow2
fdisk /dev/nbd0 -l
mount /dev/nbd0p1 /mnt/data_recovery
Once you are done, unmount it and disconnect from the network block device.
umount /mnt/data_recovery
qemu-nbd --disconnect /dev/nbd0
rmmod nbd
Unable to Use JMX Remotely for Kafka Stats
I noticed, today, that our Kafka Manager interface only shows details from one server — the one where we run Kafka Manager. We’ve done everything that we need to do in order to get this working — the port shows as open with nmap, the command to run Kafka includes all of the settings. I’ve even tried setting the JMX hostname, but still there is just one server reporting data
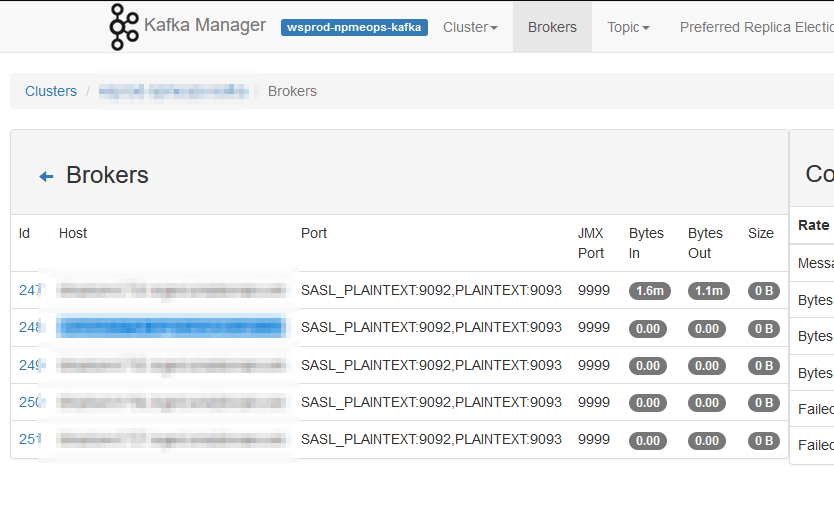
Then I happened across an article online that detailed how JMX actually uses three ports — the configured port 9999 and two other randomly selected and non-configurable ports. I used netstat to list all of the ports in use by the Java PID running my Kafka server and, voila, there were two odd-ball high ports (30000’s and 40000’s). I added those additional ports to the firewall rules and … I’ve got data for all of the Kafka servers!
This is obviously a short-term solution as the two randomly selected ports will be different when I restart the service next time. I’d prefer to leave the firewall in place (i.e. not just open all ports >1024 between the Kafka Manager host and all of the Kafka servers) so might put together a script to identify the “oddball” ports associated to the Java pid and add them to transient firewalld rules. But the last server restart was back in 2021 … so I might just manually add them after the upgrade next week and worry about something ‘better’ next year!
KDE Dolphin — Unable to Move Files and Folders
Scott was trying to move some backup files from /a/path/to/backup to /a/path/to-a-different/backup — he’s using Dolphin & has a tab open to each of the folders in question. He chown’d /a/path to his account, chmod’d /a/path so user can read and write. But using the copy/paste option … nothing happens.
I came across a few old (and closed) bugs that seemed to produce errors in this same situation — but the reporters were able to perform their copy/move operations when they used the same tab instead of having one folder open in each tab. It worked … inexplicable, but we have success!
Firewalld — Adding and Removing a Forwarding Rule
(Sorry, Anya … after today, I’ll try to not post anything about computers for three days!) Linux restricts non-root users from opening ports <1024. It’s generally a good idea not to run your services as root. Which means, unfortunately, we end up running a lot of services on nonstandard ports (so frequently that 1389 and 1636 are a quasi-standard port for LDAP and LDAPS, 8080 and 8443 quasi-standard ports for HTTP and HTTPS). But having to remember to add the nonstandard port to a web URL is an annoyance for users — I’ve seen a lot of people fix this by adding a load balanced VIP or NGINX proxy in front of the service to handle port translations. But there is a quick and easy way to handle port translation without any additional equipment. Most Linux hosts have firewalld running, and you can tell the firewall to forward the port for you. In this example, I’m letting my Kibana users access my web service using https://kibana.example.com without needing to append the :5601:
firewall-cmd –permanent –zone=public –add-forward-port=port=443:proto=tcp:toport=5601
Should you decide against the port forwarding, the same command with –remove-forward-port deregisters the rule:
firewall-cmd –zone=public –remove-forward-port=port=443:proto=tcp:toport=5601
Using the Dell 1350CN On Fedora
We picked up a really nice color laser printer — a Dell 1350CN. It was really easy to add it to my Windows computer — download driver, install, voila there’s a printer. We found instructions for using a Xerox Phaser 6000 driver. It worked perfectly on Scott’s old laptop, but we weren’t able to install the RPM on his new laptop — it insisted that a dependency wasn’t found: libstdc++.so.6 CXXABI_1.3.1
Except, checking the file, CXXABI_1.3.1 is absolutely in there:
2022-09-17 13:04:19 [lisa@fc36 ~/]# strings /usr/lib64/libstdc++.so.6 | grep CXXABI CXXABI_1.3 CXXABI_1.3.1 CXXABI_1.3.2 CXXABI_1.3.3 CXXABI_1.3.4 CXXABI_1.3.5 CXXABI_1.3.6 CXXABI_1.3.7 CXXABI_1.3.8 CXXABI_1.3.9 CXXABI_1.3.10 CXXABI_1.3.11 CXXABI_1.3.12 CXXABI_1.3.13 CXXABI_TM_1 CXXABI_FLOAT128
We’ve tried using the foo2hbpl package with the Dell 1355 driver to no avail. It would install, but we weren’t able to print. So we returned to the Xerox package.
Turns out the driver package we were trying to use is a 32-bit driver (even though the download says 32 and 64 bit). From a 32-bit perspective, we really didn’t have libstdc++ — a quick dnf install libstdc++.i686 installed the library along with some friends.
Xerox’s rpm installed without error … but, attempting to print, just yielded an error saying that the filter failed. I had Scott use ldd to test one of the filters (any of the files within /usr/lib/cups/filter/Xerox_Phaser_6000_6010/ — it indicated the “libcups.so.2” could not be found. We also needed to install the 32-bit cups-libs.i686 package. Finally, he’s able to print from Fedora 36 to the Dell 1350cn!